Forensic anthropology is an application of anatomical science (bones, skeletons etc.) of anthropology and its various sub-fields into legal matters.
In 1976, T. D. Stewart (1901–1907) defined forensic anthropology as “that branch of physical anthropology, which, for forensic purposes, deals with the identification of more or less skeletonized remains known to be, or suspected of being, human”.
Recently the scope of forensic anthropology broadens as the demand in various fields is increasing day by day. Forensic anthropology is involved in every aspect of human remains.
For a better understanding of forensic anthropology, just go through the Introduction to Anthropology.
Work of forensic anthropologists

Forensic anthropologists assist police and also works in museum and universities as researchers. They are involved in the identification of human remains (decomposed, burned, unrecognized bodies in case of mass destruction etc.) found at a crime scene or any other place.
They play important role in the death investigation. Their knowledge of the human body helps them in building a better investigation report.
When human remains are found, forensic anthropologists are called to answer the questions like-
The dead remains found belong to whom?
For how long he is dead?
How he died?
They also help in the investigation of living beings. They apply their knowledge in paternity disputes by using the method of fingerprinting.
Techniques used by forensic anthropologists
The techniques used by forensic anthropologists provide a detailed analysis of human remains. Some of the techniques are as follows-
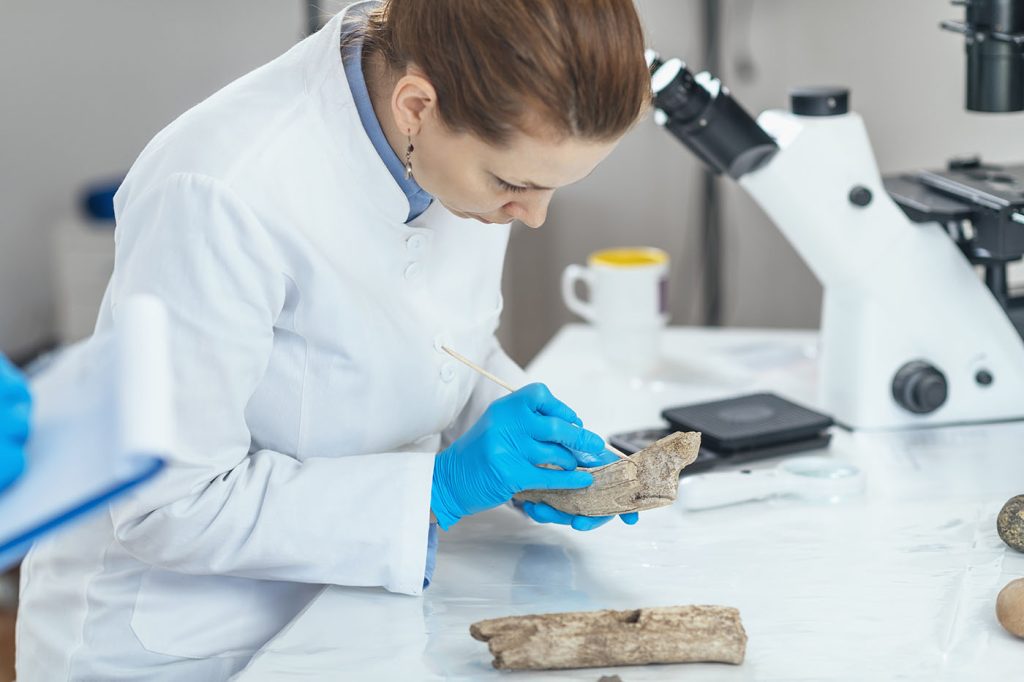

- Photography
- X-ray
- CT scan
- High powered microscope
- Chemical analysis such as the use of isotopes
- Facial reconstruction
- Fingerprinting
- DNA analysis
- Comparison of found remains with other human skeletons
Conclusion
Forensic anthropology plays a crucial part in the investigation of crime scenes. Forensic anthropologists work together to conclude from evidence found at the crime scene. This may help in mass destruction, military casualties and mass burials.
Thus the analysis by forensic anthropologists is still important. The carrier in forensics should be encouraged to a great extent.