A family is a group of people who are connected through marriage, blood or adoption. It works as a social institution. The family exists in all society. This article focus on the various aspects of the family in anthropology.
Characteristics of family
There is the head of the family which is known as “Karta”. Every member of the family gives their income to the head and then the head spends the money according to himself.
There is a joint property for the whole family and every member of the family works together. Work is distributed by the head of the family and he gives some work to each member. E.g., like in Farming.
A whole family is a unit of society.
The family has a common hearth and common religious acts.
These families are mainly Hindu families that’s why they are known as Hindu joint families. According to the Government records, such families are known as Hindu Undivided Family (HUF).
Structure of family
Based on number:
- Nuclear family- It is the family which includes the Husband, Wife and their unmarried children. It is a universal family.
Family with husband and wife are known as a semi- nuclear family.
- Extended family- Nuclear family with any extra member.
It is of two types-
Vertically extended family- When a family contains members of a minimum of 3 generations then such a family is known as a vertically extended family. It may be Patrilineal or Matrilineal.
Horizontally extended family- A family consists of uncles, aunts and cousins. In this case, the family extended horizontally across the same generation rather than vertically. It may be also Patrilineal and Matrilineal.
- Joint family- It is the part of the extended family which is a mixture of both vertical and horizontal families. It is only a feature of India.
Based on authority:
- Patriarchal- The supreme authority is with the male member.
- Matriarchal- The supreme authority is with the female member.
- Egalitarian- Here the power is equally shared by male and female members.
Based on the descent:
- Patrilineal- Family in which descent is traced through the male line.
- Matrilineal- Family in which descent is traced through the female line. For e.g., Khasi and Garo tribe of Meghalaya, Nayar of kerala
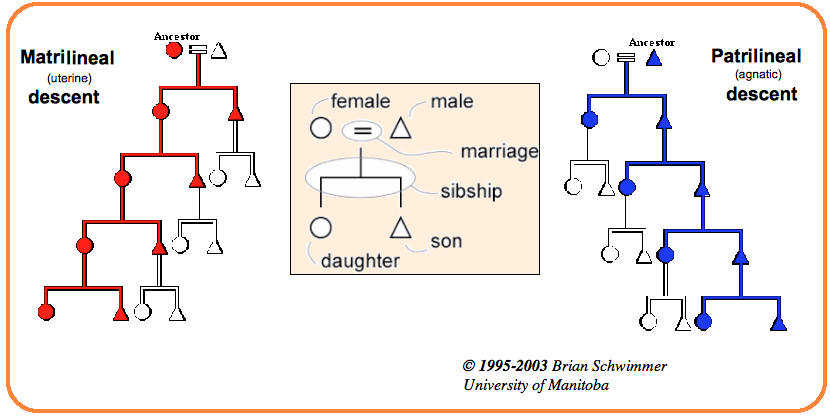
- Bilineal- Ancestry is traced through both male and female lines.
- Ambilineal- A person can trace his origin either through the male line or through the female line.
Based on residence:
- Patrilocal/ Virilocal- After marriage, husband-wife lives in husband’s father’s house.
- Matrilocal/ Uxorilocal- After marriage, the couple lives in the wife’s mother’s house. Example- Khasi, Nayar
- Ambilocal/ Bilocal- After marriage, the husband-wife either choose to live with or near any of the spouse’s parents.
- Avunculocal- Couples lives in uncle’s house after marriage.
- Neolocal– The married couple lives in the new house.
- Natolocal- The married couples live in their own houses separately after marriage.
Functions of family
According to G. P. Murdock :
- Sexual function or regulation of sex
- Reproductive function
- Economic function
- Education
Educational functions-
Family provides education related to socialization to their children. Children learn their culture gradually from their families.
Enculturation is the process by which one learns his own culture. Family make their children social beings.
Economic functions-
Family is the workshop and the children are the apprentices of this workshop.
In tribal society, children learn economic activities by observing their parents and becoming self-dependent in their economic lives. But now children learn some of their functions through family and some by other institutions.
Religious functions-
Children take part in religious practices in homes. They see such practices and try to understand their rituals, beliefs, customs etc.
Psychological and emotional functions-
It is the most important function of the family. Children get a type of emotional security in their families. They share their happiness and sadness without self-interest, greed and dishonesty. They feel safe together.
Other functions are as follows:
Health-related
Recreational function
Cultural function
Social-emotional support
Inter-institutional linkage
Status transmission
Common habitation
Read more:
- The Maharaj Libel Case of 1862: A Landmark in Colonial Legal and Social History
- Acclimatization: The Subtle Dance Between Humans and Their Environment
- The Anthropology of Sleep
- Lamarck’s Theory of Evolution
- Bipedalism and Structural Changes