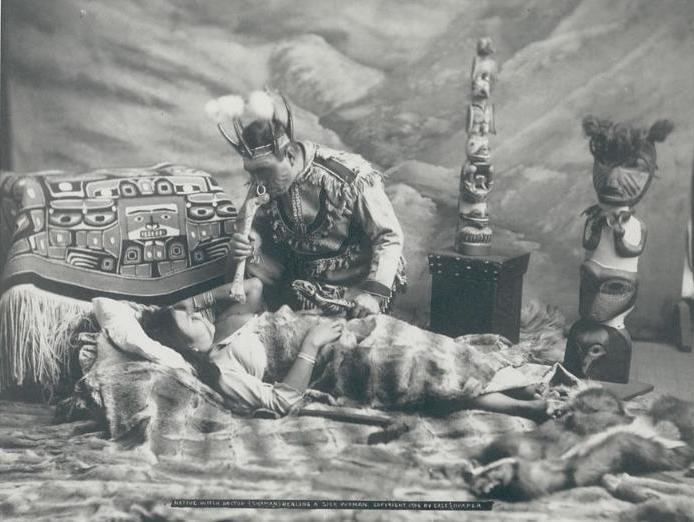
Anthropology of Heritage involves the management of natural heritage and cultural resources. Heritage is important as it is common in the whole world. There is a need to care for and preserve our heritage for peace and harmony which is why there are various international conventions for the protection of heritage. Heritage includes both natural and cultural heritage.
According to the UNESCO-
Natural heritage- Natural heritage refers to natural features, geological and physiographical formations and delineated areas that constitute the habitat of threatened species of animals and plants and natural sites of value from the point of view of science, conservation or natural beauty.
Cultural Heritage- Cultural heritage includes artefacts, monuments, a group of buildings and sites, and museums with diverse values including symbolic, historical, artistic, aesthetic, ethnological or anthropological, scientific and social significance.
Cultural heritage
Cultural heritage is inherited from the previous generations to the future generation. It allows people to identify with others having similar backgrounds. It gives a sense of belonging to a community. It helps in sustaining cultural diversity.
Cultural heritage splits into two categories. These are-
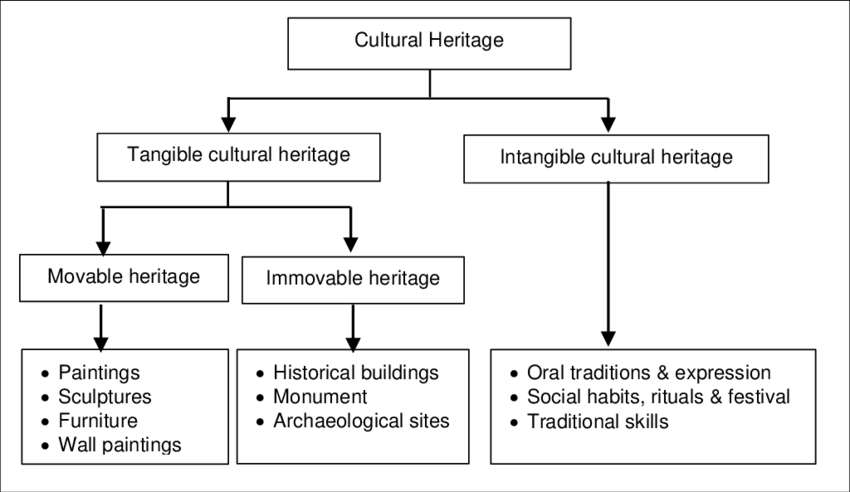
Tangible cultural heritage and Non-Tangible cultural heritage. Tangible heritage represents artefacts, monuments, buildings, landscapes etc. while Intangible represents values, traditions, food, language, literature, beliefs, performing arts, festive events, folklore, oral history etc. Cultural tangible heritage has a physical presence while intangible has no physical presence. Both tangible and intangible heritage are connected.
Anthropology and Heritage
Anthropology of heritage focuses on historical archaeology. It explains the role of heritage in the past and its relevance in the present day. It emphasizes the legacy of the past. Anthropology engaged in the ethnographic study of heritage sites, cultural objects, artefacts and their relation with the community.
It does address the questions like what is the anthropogenic role in preserving the heritage as well as in the destruction of heritage? How we can lower the pace of destruction of heritage? How do innovative collaborations protect our rich heritage? What is the impact of all the studies and research done for heritage on the local population?
Various governmental and non-governmental organizations work for both natural and cultural heritage preservation.
Some of the organizations and institutions that work to protect cultural heritage :
- UNESCO World Heritage Centre
- U.S. Committee of the Blue Shield
- Archaeological Institute of America
- Society for American Archaeology
- SAFE (Saving Antiquities For Everyone)
- United States Department of State, Bureau of Educational And Cultural Affairs- Cultural Heritage Center)
Some of the Organizations in India:
- National Center For Performing Arts (NCPA)
- Indian National Trust for Art and Cultural Heritage (INTACH)
- Society For The Promotion of Indian Classical Music And Culture Amongst Youth (SPIC MACAY)
- Indian Numismatic Historical and Cultural Research Foundation (INHCRF)
- NGO- Kalamandir
The World Heritage Convention
It is an international treaty called the Convention concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage, adopted by UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization) in 1972.
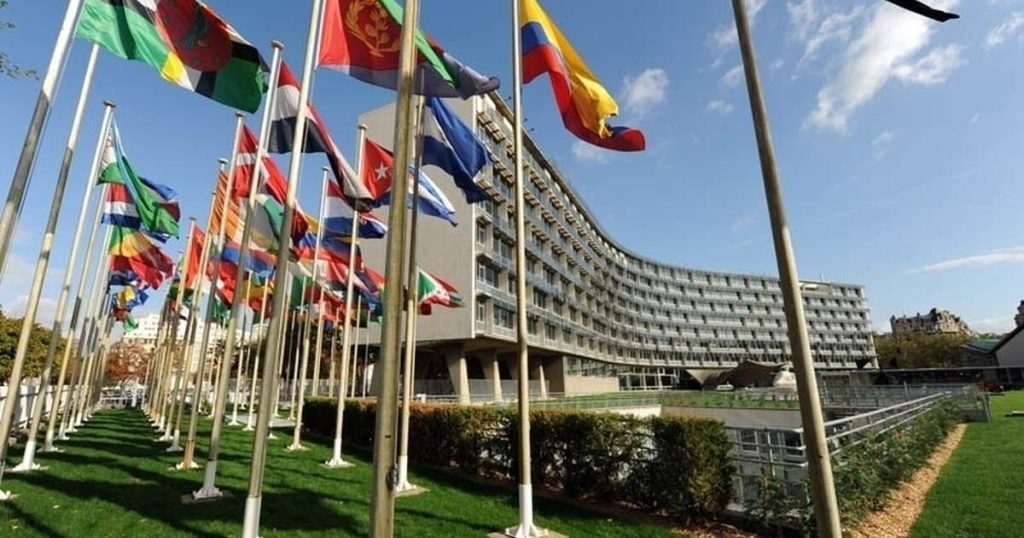

The aim is to increase the cooperation between member countries for the protection of heritage. It links the concept of nature conservation and the preservation of cultural properties. It recognizes how people interact with nature and there is a need for balance between them.
Conclusion
In recent times, heritage has become a centre for protection through the efforts of governmental and non-governmental agencies. They aim to bring all the related experts on the same platform to work for the preservation of our cultural heritage. There is a need to explore the relationship of heritage with other disciplines.
There is a need to change the approach for better results. New heritage policies and initiatives are required. Participation of the local people and the experiences of the experts is helpful. There is a need to shorten the gap between government policies and civil society.
The Anthropological Study of heritage concerns the participatory mode between organisations or institutions and locals.
References:
Anthropology and heritage studies
The Significance of Cultural Heritage







