In almost all the societies of the world, individuals are connected based on various relations, this relation is called kinship. The anthropology of the kinship system is formed by family and marriage.
According to Charles Winick in ‘The Dictionary of Anthropology’, the Kinship system may include socially recognized relationships based on supposed as well as actual genealogical ties.
According to the anthropologist George Peter Murdock: “Kinship is a structured system of relationships in which kins are bound to one another by complex interlocking ties”.
According to D.N. Majumdar in “An introduction to social anthropology”, in all societies individuals and groups are bound with each other based on different types of relationships, the most universal and basic relationship among them is kinship.
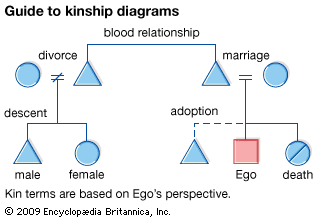
The kinship system is the basis of heredity and the principle by which this kinship heredity is determined is called the descent principle. People who are connected by kinship are called kin and that whole group is called the kin group. The ego is the individual who forms the central reference point in a kinship diagram.
Importance of kinship system
- The kinship relationship classifies individuals and relatives based on the terminological system.
- The kinship system regulates an individual’s rights and behaviour.
- Kinship defines the role and status of individuals.
- Based on cooperation, the system of kinship creates closeness and unity among the relatives, which is necessary for the personal protection of its members.
- It also provides financial security to the individual by the description and transfer of property based on rules of succession and kinship.
Thus kinship system is not a group but it is the basis of family and descent groups.
Types of kinship
Consanguineal kinship
This kinship is based on blood. For example- the relationship between parents and children, between siblings etc.
Affinal kinship
This is based on marriage. Example- relation between husband and wife.
Fictive kinship
This is not based on marriage or blood. These are fictional relations. For example- relations between friends, the relation between informally adopted kids and their parents and many other such relations.
Degree of kinship
Murdock has given three degrees of kinship-
- Primary kinship
- Secondary kinship
- Tertiary kinship
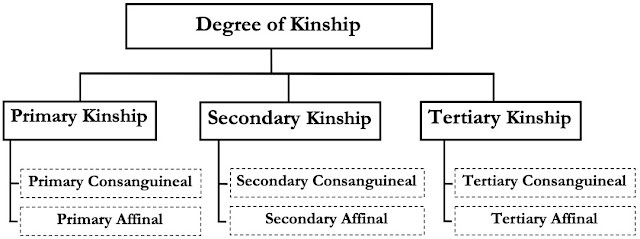
Primary kinship is available among the members of the nuclear family. It is direct relations. It is of 8 types out of which 7 are consanguineal and one is affinal.
Consanguineal= father-husband, father-daughter, mother-son, mother-daughter, brother-sister, sister-sister, brother-sister.
Affinal= husband-wife
Secondary kinship is that kinship which is close to the primary relation i.e. ‘primary relative of the primary relation’. There are 33 types of secondary kinship which include both consanguineal and affinal kinship. Examples- father’s brother, sister’s husband etc.
Tertiary kinship is those relations that are a secondary relative of a primary relative or a primary relative of a secondary relative. There are 151 types which include both consanguineal and affinal kinship. Example- the relationship between great-grandparents and their great-grandchildren etc.
Kinship terms
Kinship terms refer to the words by which kinship relatives are called or understood. Kinship terms are divided into three grounds.
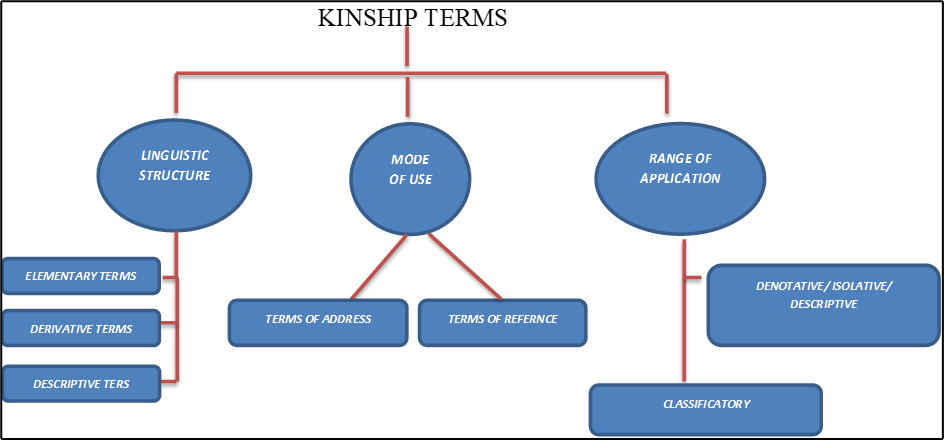
Based on linguistic structure
3 types-
- Elementary terms- Those terms which cannot be further broken down into smaller ones are called elementary terms. Examples- mother, father, son etc.
- Derivative terms- When a suffix or prefix of an adjective is added in elementary terms then we get derivative terms. Examples- grandfather, father-in-law, sister-in-law etc.
- Descriptive terms- Those kinship terms which are formed by the combination of two or more elementary terms are known as descriptive terms. Examples- mother’s brother’s son, father’s sister’s daughter etc.
Based on the mode of use
2 types-
- Terms of reference- Kinship terms which are used by us for indirectly referring to a person are known as kinship terms of reference. Examples- mother, father, son, daughter etc.
- Terms of address- Kinship terms which are used by us for addressing our kins or relatives are known as terms of address. Examples- father- daddy or papa, mother- mamma or mummy etc.
Based on usage
2 types-
- Descriptive terms- Those kinship terms that indicate a particular relationship are also called descriptive terms. For example- the term ‘mother’ and ‘father’ are used only for parents.
- Classificatory terms- Those kinship terms that indicate more than one relationship is known as classificatory terms. For example- cousin (used for father’s brother’s son, father’s sister’s son, mother’s sister’s daughter etc.), uncle (used for mother’s brother, father’s brother, mother,’s sister’s husband etc.).
Other terms related to kinship
Agnates– All relatives related to the male member
Uterine kins– when descent is traced through the female line
Cognates– people sharing a common ancestor
Read more
- The Maharaj Libel Case of 1862: A Landmark in Colonial Legal and Social History
- Acclimatization: The Subtle Dance Between Humans and Their Environment
- The Anthropology of Sleep
- Lamarck’s Theory of Evolution
- Bipedalism and Structural Changes
Also, read
You should know about India’s first private rocket launch: VIKRAM-S







