Cultural evolution- Theory of Cultural change may be defined as a process by which different successive forms in socio-cultural Institutions or the culture of mankind as a whole are developed and accumulated to constituted the growth of culture over different periods but in continuity.
Other theories of cultural change are Diffusion theory and Acculturation theory.
The methodology of cultural evolution contains two vitally important assumptions- first, it postulates that genuine cultural parallel or cultural similarities developed independently in all cultures in historical sequences. Second, it assumes that parallels or similarities developed independently due to the Psychic Unity of Mankind. Thus, cultural evolution may be defined as a quest for cultural similarities or cultural parallels or cultural regularities.
Typology of Cultural Evolution
There are mainly two typologies of cultural evolution-
- Classical Evolutionary theories
- Neo-Evolutionary theories
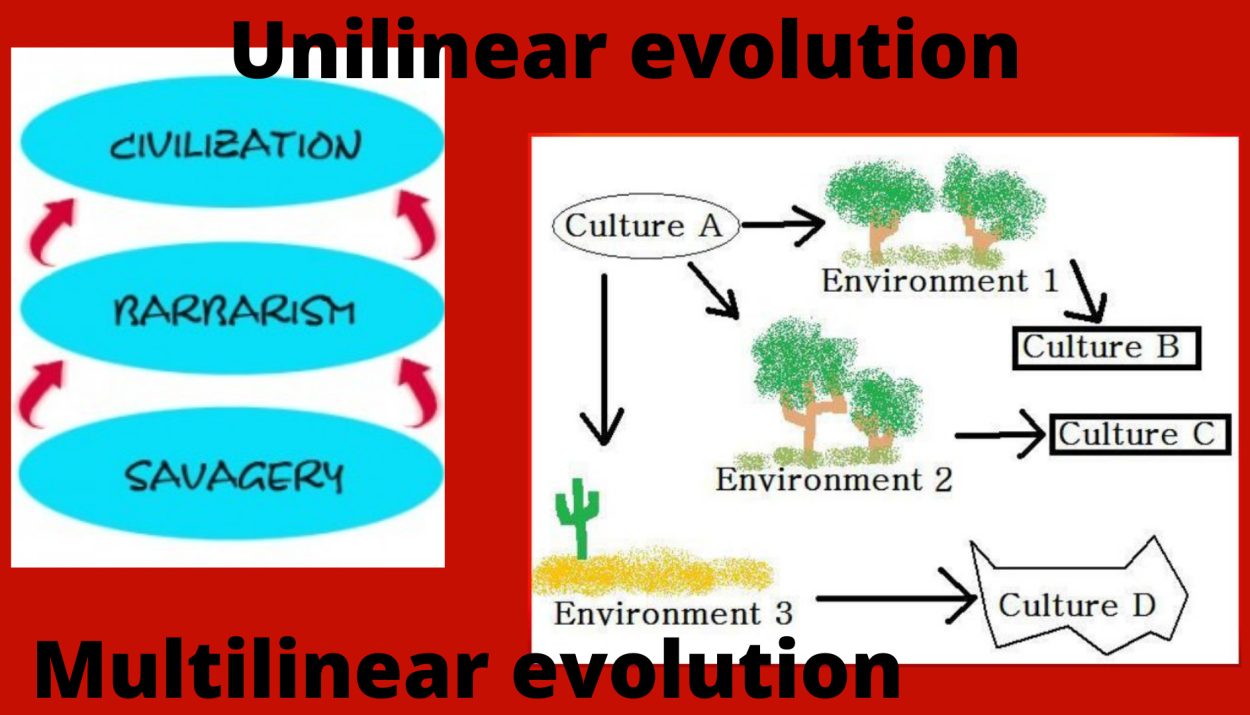
Classical Evolutionary theories
Also known as Unilinear Evolution or Historical Method or Comparative Method
This theory was propounded by E. B. Tylor, H. J. S. Maine, J. F. McLennan, J. Frazer (all British Evolutionists); L. H. Morgan (American Evolutionists); J. J. Bachofen, A. Bastian (German Evolutionists).
Salient features of this approach are as follows-
- Human culture as a whole or socio-cultural institution, evolve in unilinear sequence, stage after stage.
- The direction of cultural evolution is from simple to complex, from similarity to dissimilarity and from indefinite to definite.
- Different stages of evolution can be established by speculating historical explanations and by using the comparative method.
- Similarities in culture traits, culture complexes and cultural patterns of the World are caused by the psychic unity of mankind and parallel inventions.
- The psychic unity of mankind means while living in similar physical and climatic conditions and environments, human beings think similarly for solutions to various problems. Due to this, parallel inventions take place.
- Cultural diversities do not occupy a significant place in the unilinear evolutionary schemes.
- In the higher stage of culture, some residues of primitive stages can be seen, which are termed as survivals and which remind about the earlier stage of the culture.
Tylor’s View
He talked about Unilinear Cultural Evolution, in his book- ‘Primitive Culture (1871)’.
His theme was the Study of Evolution of Culture.
His criteria were techno-organic criteria and Cultural criteria.
His technique was (i) Techno-organic theory/ Techno-economic theory/ Historical Materialism
(ii) Comparative Criteria/ Historical Method
He believed in the psychic unity of mankind/ mental unity and cultural survivals.
He gave the reason why he preferred to study evolution in the field of culture. He said that it is very hard to investigate the evolution in social fields or society because it needs application, a very good scientific methodology like ‘Statistical method’, ‘Comparative method’ etc. But, the Statistical method was not known till then.
Tylor said that by Comparative Method, comparative conclusions can be given; good and better can be decided.
He gave the evolutionary sequence of religion, as follows-
Animism
Polytheism
Monotheism
Morgan’s View
He talked about unilinear Social and Cultural evolution in his book ‘Ancient Society: Researchers in lines of human progress from savagery through barbarism to civilization (1877)’.
His theme was the Study of Society and Culture.
His criterion was Cultural Criteria.
He believed in the psychic unity of mankind/ mental unity.
He did not believe in Cultural survival.
He used the Comparative method.
He believed that all discoveries and inventions are socially connected and can be placed in the social order.
He did not deal with the continuous phase of civilization. He dealt with civilization in earlier phases. He did not deal with modern society but with the ancient society while Tylor studied cultural evolution right from the evolution of man up to the continuous phase of civilization.
He studied cultural evolution by the changes in the institutions of society. Tylor studied cultural evolution only in religion and magic.
He talked about the unilinear evolutionary sequence of Family/ Marriage as-
Consanguineous marriage
Punaluan/ group marriage
Syndesmian marriage
Polygyny
Monogamy
Evolution of different institutions
Culture
Savagery
Barbarism
Civilization
Marriage
Monogamy
Promiscuity
Sex communism
Family
(by Henri Maine in ‘System of Consanguinity and Affinity in Human Family’ 1870)
Consanguine family
Punaluan/ group family
Syndyasmian family
Polygamous family
Monogamous family
Society and Descent
(by Henri Maine in his book ‘Ancient Law’ 1861, Morgan, McLennan, Bachofen)
Matrilineal and Matriarchal
Patrilineal and Patriarchal
Kinship Terminology
(By Morgan in his book ‘League of Iroquois’ 1851)
Classificatory terminology
Descriptive terminology
Law
(By- Henri Maine in his book ‘Ancient Law’ 1861)
Civil law
Criminal law
State
(By- Henri Maine in his book ‘Ancient Law’ 1861)
Band
Kinship based Political Structure
State
Property
(By- Henri Maine in his book ‘Ancient Law’ 1861)
Communal
Personal
Religion
(By- E. B. Tylor)
Animism
Polytheism
Monotheism
Art
(By- A. C. Haddon in his book ‘ Evolution in Art’ 1895)
Realistic
Symbolic, Algebraic
Economy
Food Gathering and Hunting
Pastoral
Agriculture
Industry
Science
(by- James Frazor)
Magic
Religion
Science
Weaknesses of this approach are as follows:-
- These evolutionists mostly tried to show independent evolution of culture stage after stage or period after period in sequence.
- These evolutionists have accepted that the origin of similar cultural traits was due to a similar cause. This assumption of classical evolutionists is also a subject of criticism because human history is a witness that different cultures have originated in the same geographical environment.
- The claim of these scholars, that mankind of the world has passed through different stages or periods of cultural development in sequence, also does not stand true for all cultural or social groups.
- The scholars were so biased with their preconceptions that they forget the theory of diffusion or migration of culture traits.
- The classical evolutionists also neglected the importance of discovery or invention.
Neo Evolutionary Theory
The neo-evolutionists told that evolution is in form of a parabolic curve.
Main scholars of this approach are V. G. Childe (Bristish scholar); Leslie white, J. Steward (American Evolutionists). this approach has two sub approaches-
- Universal Cultural Evolution
- Multilineal Evolution
Universal Cultural Evolution
The evolution of culture has taken place universally, here universal means that the evolution of culture may have happened all over the world, it may have happened more or less somewhere. At the same time, it may also be that the order of evolution has been different according to the cultures. Evolution is a universal phenomenon, that is why we should study the cultural universal evolution and not the particular culture. That is why their theory is called Universal Cultural Evolutionary Theory.
Universal events must have been responsible for universal evolution and these events may have been different according to cultures.
There appear to be two approaches to Universal Cultural Evolutionary Theory. These are-
- Archaeological approach– Given by V.G. Childe
- Energy capture approach– Given by L. White
V. Gorden Childe
In his book- ‘Social Evolution (1951, New York)’, he gave the following evolutionary sequence-
Archaeological sequence Cultural sequence
Palaeolithic Period Savagery
Neolithic Period Barbarism
Copper Period Higher Barbarism
Early Bronze age Civilization
Leslie White
In his book- ‘The Science of Culture’ (1949) and ‘The Evolution of Culture’ (1959), he dealt with neo-evolution. His basic strategy was Cultural Materialism. Following are some points of his theory-
- Culture is created by man and is dependent on man for its existence.
- Energy is required to run any type of life, thus life can be understood as the process of acquiring or using energy.
- Culture is a system that acts as a means of obtaining and using energy.
- He gave the theory that as the use of energy per person per year in the culture increases, the culture will also develop and this change is the Cultural evolution.
- In this way, he laid great emphasis on the material aspect of culture, hence his theory is known as cultural materialism.
- For him, processes related to the socio-cultural system consists of three segments-
- Techno-economic sub-system= material aspect
- Social sub-system= family, marriage, kinship, social unit, behaviour etc.= non-material aspect
- Ideological/ Philosophical sub-system= ideas, morals, knowledge, arts, attitudes, views etc.= core of culture= non-material aspect
According to him, the technological sub-system prevails over others. It is the key sub-system. It decides the whole socio-cultural system.
He showed the stage of development as-
Savagery
Barbarism
Civilization
Energy Revolution
He showed the stage of development of societies as follows-
Hunting and Food gathering
Pastoral society
Farming society
Industrial society
The technological sub-system controls the amount of energy captured and utilized by the cultural system. He said, “Culture advances as the amount of energy harnessed per capita per year increases or as the efficiency or economy of the means of controlling energy are increased or both”. This law of cultural development can be expressed as a formula, which is,
- E. T= C,
Where E is energy harnessed by the people in a culture per capita per year
- Is technology; efficiency of tools/ artefacts/ technology which is employed by the people, first for harnessing the energy and secondly, for utilizing it for the specific purpose to ensure their survival/social existence.
- Is cultural development; level of culture or state of development culture at a particular time.
- N. P. R= S,
Where N is Nutrition
P is Protection
R is Reproduction
S is a social organization
- T. L= P,
Where T is Things
L is labour
P is Property
Note- White told about Spontaneous Change and Planned/ Directed/ Sponsored Change.
Spontaneous Change: this is a natural mode of change.
Planned Change: this is planned and directed change.
Spontaneous change+ Directed change= Cultural change
Mutlilinear Evolution
This theory was developed by J. Steward. He believed that all cultures of the world have not passed through the same development stage, rather their stages were different in different areas or sub-areas. Thus, this theory is a methodology based on assumption that significant regularities or parallels occur in cultural change, and it is concerned with the determination of cultural laws. Its method is empirical rather than deductive.
The environment has an integral contribution to the evolution of culture. Because he laid great emphasis on ecology, that is why his theory is also called the ecological approach, the evolution of culture is according to ecology and technology. The evolution of culture is according to ecology and technology.
Cultural adoption is also of great importance in cultural development and cultural evolution, the culture that adapts things in a better way, the evolution of that culture is faster.
To study in detail go through the article- Ecological Anthropology
Read more
- The Maharaj Libel Case of 1862: A Landmark in Colonial Legal and Social History
- Acclimatization: The Subtle Dance Between Humans and Their Environment
- The Anthropology of Sleep
- Lamarck’s Theory of Evolution
- Bipedalism and Structural Changes
Also read-
Sources of e-waste and its effect on health and the environment