According to the Cambridge Dictionary, “Descent is defined as the state or fact of being related to a particular person or group of people who lived in the past”. It is the sociological linking of children to their parents. Descent tells a person’s family origin.
Murdock- “Descent refers to a cultural principle whereby an individual is socially allocated to a specific group of consanguineal kinsmen”.
Meyer Fortes– “A descent group is an arrangement of persons that serves the attainment of legitimate social and personal ends”.
To know the basics about kinship in anthropology, read this article- Anthropology of Kinship
The descent principle refers to the principle based on which ancestry is determined. Descent rules link individuals to a specific set of relatives through known or presumed common ancestry. Descent rules vary from society to society.
In some societies, the descent is determined by the father, in some by the mother, and in some by both, the group of one descent is called the descent group.
Types of descent
Unilateral descent and Bilateral descent
Unilateral descent
Here the person’s descent is traced through either father’s or mother’s line. It is classified into two groups-
Patrilineal descent: Descent is traced through the male line from father to son. The son inherits the status, name and property of his father.
Matrilineal descent: Descent is traced through the female line from mother to daughter. The children of both sexes belong to their mother’s descent group but only the daughter inherits the name, status and property of her mother.
Bilateral descent
The person’s descent is traced through both the male and female lines. The descent rules are distributed equally through both parents.
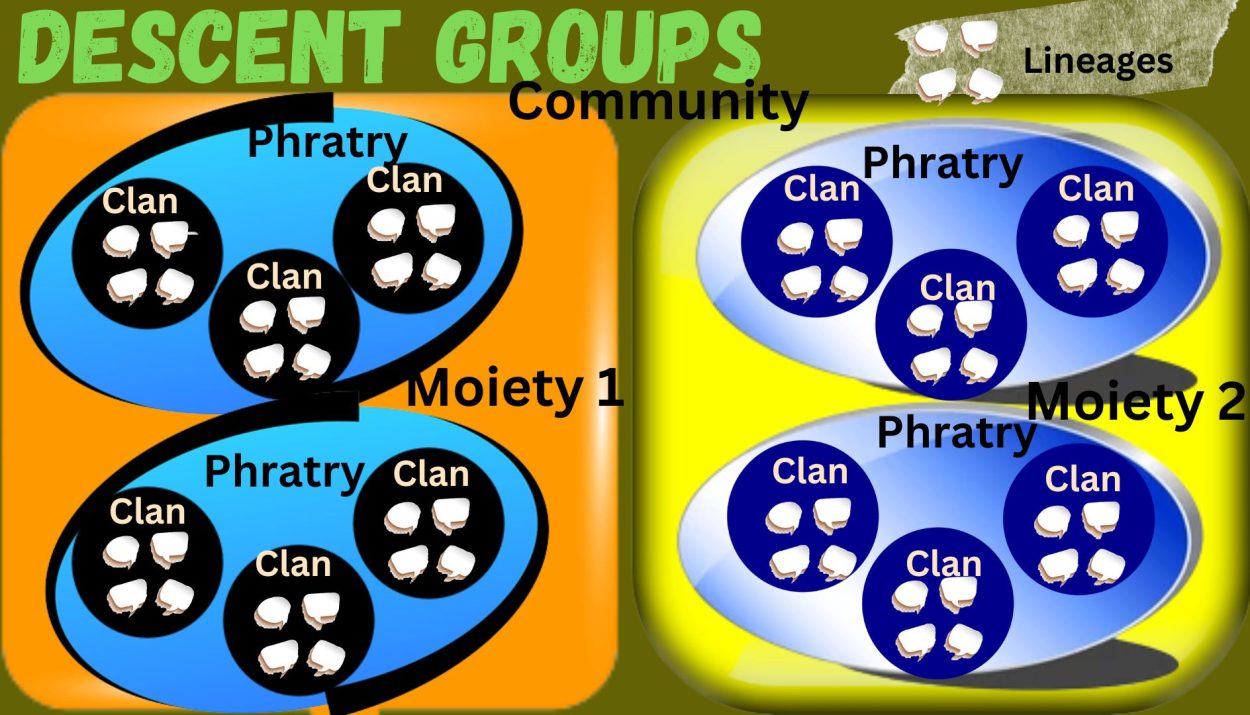
Descent groups
The descent groups consist of persons who are genealogically connected through a common ancestor. Some of the important descent groups are as follows-
Lineage
Clan
Phratry
Moiety
Each moiety is divided into several phratries. Each phratry is further divided into many clans and each clan is into several lineages. At last, each lineage is split into a number of families.
Lineage
A group of relatives who trace their descent from a single ancestor is called lineage. The special thing is that their ancestor is not imaginary but real. Normally there are 5 generations in lineage. Lineage is unilateral descent and exogamous group.
(In endogamous groups marriage within one’s social group is permitted while in exogamous groups marriage outside the group is allowed. Exogamy prohibits marriage within an individual’s immediate social group. The caste groups of India are traditionally exogamous).
The member of one lineage group has common blood linkage and traced their descent through common ancestry to a single person. Here the ancestor existed in reality.
It can be traced from either the father’s or the mother’s side. On this basis, lineage can be of two types-
Patrilineal lineage i.e. lineage is traced from the father’s side.
Matrilineal lineage i.e. lineage is traced through the mother’s side.
kindred is formed by mixing these two. That is, a kindred is a group of relatives. Lineage is most important in human life. It plays a significant role in various types of events like marriage, festivals etc.
Clan
The largest group of relatives that traces its origin from a hypothetical ancestor is called a clan. Who is this ancestor and where will he be coming from, it can only be imagined. Here the common ancestor may be mythical like a saint (in the case of Hindu society) or it may be totemic things like tigers, fish etc. They have their totem and spread far and wide.
A group of lineage forms a clan. It is also a unilateral descent group and an exogamous group.
The clan is termed “Gotra” in Hindu society. The most important thing is that most people do not have knowledge of their gotra and when asked, they can tell little about their gotra. It is not used in our day-to-day life but it is important in a marriage alliance. Marriage is prohibited within a gotra.
Phratry
A phratry is bigger than a clan. The literal meaning of Phratry in Hindi is brotherhood.
It has been seen in some tribals that due to some natural calamity or other reasons many people of the clan die, in such cases two-four gotras together form a new unit. This is called phratry.
Like clan, phratry is also unilineal and exogamous.
Examples- Munda, Ho, Oraon etc. (all are tribes of India)
Moiety
In some communities, it is found that the whole community splits into two unilateral descent groups and these are called two different Moieties. This system is called a dual organization. This means that it shows two groups of kinship. The members of one moiety are allowed to marry members of other moieties.
For example- The Toda and Bhil are tribal groups in India and both are divided into two Moieties.